| Back to the main index |
|
After the famous IS-3 and IS-4 the development of the Soviet heavy tanks did not stop at the experimental IS-5 and IS-6. With the experience gained at war and during the development of the earlier models, Cheliabinsk designers attained a new task, the creation of the new and mighty tank, outlined still in 1945 when Kotin signed the project on September 9.
 |
Technical data Weight - 68 to |
The draft provided for design, performed along the guidelines laid by IS-3 and included thick armor and traditional 122-mm gun.

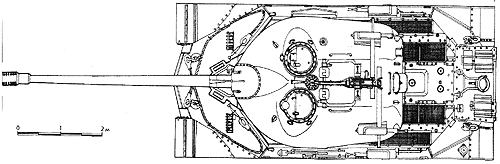
The tank had the smooth lines of turret and hull. . Numerous alternation and innovations were introduced in the design of the hull, engine and suspension
Due to the absence of the passable engine, the draft provided the installation of two engines. The tank should have the electric transmission tested at IS-6.
Reminding the Flying Fortress, the tank was to be armed with an enormous number of machine guns-8, one of them was installed in the small turret in the rear part of the main turret. All machine guns were remotely controlled, incl. AA-MG on the top of the turret.
The tank had automatic fire extinguishers and semi-automatic loading system of the main gun. The suspension had modified and shortened 7-thread torsion, short enough to allow the installment of engine between them. Double action shock absorbers were placed in the hollow suspension levers. For the first time on the Soviet heavy tanks only the wheels of big diameter were used without suspending rollers.
Two first prototypes were finished on Dec. 8 and 25, 1946.
The works on the new tank developed in two steps, in Cheliabinsk and Leningrad.
With the return of the Kirov's plant back to Leningrad, the works on the project were transferred from Cheliabinsk to Leningrad. The works were continued during 1947 and the original plan was sufficiently modified, partly due to the local conditions, party because it was initially a Cheliabinsk design.

The tank received new ex-ship 130-mm S-70 main gun with new fire control system and stabilization. The rear turreted MG was gone. The number of fuel tanks was reduced.
Finally, the modified ship engine was installed with the respective changes to the design of the hull. Having 1050 HP, the engine allowed the tank to move with the speed of 60 km/h. The tank was said to be as easy in driving as a car due to the numerous hydraulic power drives.
With its 68-ton weight the tank was, indeed, heavy. The front armor of the turret was 210-mm thick. The testing proved that not only the deadly 12.8-cm gun of Jagdtiger but even own 130-mm gun could not take out IS-7 at the combat distances.
It is not clear how the designers intended to overcome the difficulties with the railway authorities because the maximum cargo weight was still 55 ton and, in fact, some sources indicate that there were heavy disputes. Nevertheless, two test tanks were built. Despite the fact that the control and tracking system was ready, the machine gun in the automatic rear turret was omitted. After practical test in 1948 there was a decision to build 50 tanks.
Due to the reasons unknown, most likely because of the political repression against Leningrad bosses in the same year, the tank never reached the production lines.
It is sometimes considered one of the best Soviet heavy tank designs and one the mightiest ever. The experience and aggregates developed in process were used on many later designs.